Virtual Local Area Network(VLAN):-
A virtual local area network (VLAN) is a logical group of workstations, servers and network devices that appear to be on the same LAN despite their geographical distribution. A VLAN allows a network of computers and users to communicate in a simulated environment as if they exist in a single LAN and are sharing a single broadcast and multicast domain. VLANs are implemented to achieve scalability, security and ease of network management and can quickly adapt to change in network requirements and relocation of workstations and server nodes. When you create VLAN you are given the ability to create smaller broadcast domain within a layer2 switch internetwork by assign different ports on the switch to different subnet. By default host in a specific VLAN can’t communicate with the host that are members of another VLAN. So if you want inter VLAN communication then you still need a Layer 3 device.
VLAN aims and benefits
- VLANs facilitate easy administration of logical groups of stations that can communicate as if they were on the same LAN. They also facilitate easier administration of moves, adds, and changes in members of these groups.
- Traffic between VLANs is restricted. Bridges forward unicast, multicast, and broadcast traffic only on individual LANs that serve the VLAN to which the traffic belongs.
- As far as possible, VLANs maintain compatibility with existing bridges and end stations.
VLAN TERMS :-
VLAN ID
A unique number (between 1 and 4095) that identifies a particular VLAN.
VLAN Name
A 32-character alphanumeric name associated with a VLAN ID. The VLAN Name is intended to make user-defined VLANs easier to identify and remember.
Tag Header (VLAN Tag)
A field within a frame that identifies the VLAN the frame has been classified into. The Tag Header is inserted into the frame directly after the Source MAC address field. Twelve bits of the Tag Header are the VLAN ID. The remaining bits are other control information.
Tagged Frame
A data frame that contains a Tag Header. The Tag Header can be added to the data frame by a VLAN aware switch to any frame received from a port that is a member of a VLAN.
Untagged Frame
A data frame that does not have a Tag Header inserted into it.
Default VLAN
The VLAN to which all ports are assigned upon initialization. The Default VLAN has a VLAN ID of 1.
VLAN Trunks
A trunk link, however, can transport more than one VLAN through a single switch port (Trunk Link Carry all the VLAN or Bypass every VLAN). Trunk links are most beneficial when switches are connected to other switches or switches are connected to routers. A trunk link is not assigned to a specific VLAN. Instead, one, many, or all active VLANs can be transported between switches using a single physical trunk link.
Connecting two switches with separate physical links for each VLAN is possible. As VLANs are added to a network, the number of links can quickly grow. A more efficient use of physical interfaces and cabling involves the use of trunking. Cisco supports trunking on Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet switch links, as well as aggregated Fast and Gigabit EtherChannel links. To distinguish between traffic belonging to different VLANs on a trunk link, the switch must have a method of identifying each frame with the appropriate VLAN. Several available identification methods are discussed in the next section.
VLAN Frame Identification
Because a trunk link can transport many VLANs, a switch must identify frames with their VLANs as they are sent and received over a trunk link. Frame identification, or tagging, assigns a unique user-defined ID to each frame transported on a trunk link. Think of this ID as the VLAN number or VLAN “color,” as if each VLAN was drawn on a network diagram in a unique color. VLAN identification can be performed using two methods, each using a different frame identifier mechanism:
Inter-Switch Link (ISL) protocol
- IEEE 802.1Q protocol
Inter-Switch Link Protocol
The Inter-Switch Link (ISL) protocol is a Cisco proprietary method for preserving the source VLAN identification of frames passing over a trunk link. ISL performs frame identification in Layer 2 by encapsulating each frame between a header and trailer. When a frame is destined out a trunk link to another switch or router, ISL adds a 26-byte header and a 4-byte trailer to the frame. The source VLAN is identified with a 10-bit VLAN ID field in the header. The trailer contains a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) value to ensure the data integrity of the new encapsulated frame. If a frame is destined for an access link, the ISL encapsulation (both header and trailer) is not rewritten into the frame before transmission.
IEEE 802.1Q Protocol
Instead of encapsulating each frame with a VLAN ID header and trailer, 802.1Q embeds its tagging information within the Layer 2 frame. This method is referred to as single-tagging or internal tagging. 802.1Q also introduces the concept of a native VLAN on a trunk. Frames belonging to this VLAN are not encapsulated with any tagging information. In the event that an end station is connected to an 802.1Q trunk link, the end station can receive and understand only the native VLAN frames. This provides a simple way to offer full trunk encapsulation to the devices that can understand it, while giving normal access stations some inherent connectivity over the trunk.
Types of VLANs:-
- Static VLANs
- Dynamic VLANs
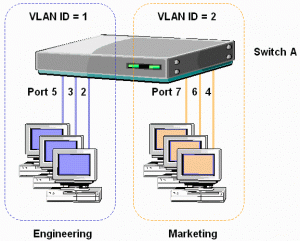
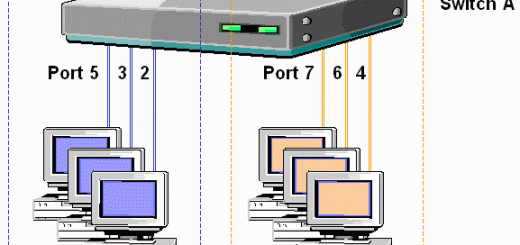
Static VLANs are specified by switch port. For example, a 12 port fast ethernet switch is split for the creation of 2 VLANs. The first 6 ports are associated with VLAN1 and the last 6 ports are associated with VLAN2. If a machine is moved from port 3 to port 11, it will effectively change VLANs.
Dynamic VLANs are specified by MAC address. Assuming the same scenario, a system administrator will enter MAC addresses for all machines connecting to the switch. These addresses will be stored in a memory chip inside the switch that forms a database of local MAC addresses. Each MAC address can then be associated with a certain VLAN. This way, if a machine is moved, it will retain the original VLAN membership regardless of its port number.
- If we want to add a second VLAN, we don’t need a second switch.
- We simply create another VLAN on the same switch and assign the desired ports to that VLAN (we change the port/native VLAN on the desired ports).
- The switch’s filtering database maintains the port-to-VLAN mapping.
- This diagram is analogous to having two separate switches or LAN segments.
Native VLAN :-
A topic that causes considerable confusion is the native VLAN. The native VLAN is a term used with interfaces that are configured as VLAN trunks. When a switch port is configured as a trunk, it tags frames with the appropriate VLAN number. Frames from all VLANs are carried across the trunk link containing the 802.1Q or ISL tag, except for frames belonging to VLAN 1. By default, frames from VLAN 1 belong to native VLAN, and are carried across the trunk untagged. Frames from the native VLAN, VLAN 1, are carried across this trunk link untagged.
The native VLAN can be modified to a VLAN other than VLAN 1 with the following interface command:
Switch(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id
It is recommended that the native VLAN should never be used as a user VLAN or the management VLAN.






Hi there, You have dopne a fantastic job. I will definitely digg itt and personally
recommend to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this website.
Terrific post but I was wanting to know if you could write a
litte more on this subject? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit more.
Kudos!
Look at my web blog SteviePOlten
Your thing is very unique when compared with other folks I have
got read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you’ve
got the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this page.
Also visit my blog post: JoeyMAanerud
What’s up mates, good post and fastidious arguments commented at this place, I am really enjoying by these.
My homepage: KeliJTwersky
Business personality gives a fresh utilize their Facebook marketing.
By advertising with Facebook, you’re not just simply there to obtain giant varieties of fans ‘liking’ your
own personal FB page, but to make a group of folks who can come to be buyers.
If this appears like something you desire for the site, why don’t you
join with Kontera here.
As it been found, these menial assignments didn’t last just a couple of days nevertheless for greater year.
However, as long as they needed Trump, after over ten years running a business, that will provide me some concern. This is
approximately starting the process of to become listed on an MLM or Network Marketing business to make
another individual rich selling and promoting their goods for the children instead of starting your
venture and branding yourself and your individual products.